Smart Ways to Understand Perfect Price Discrimination in 2025
“`html
Smart Ways to Understand Perfect Price Discrimination in 2025
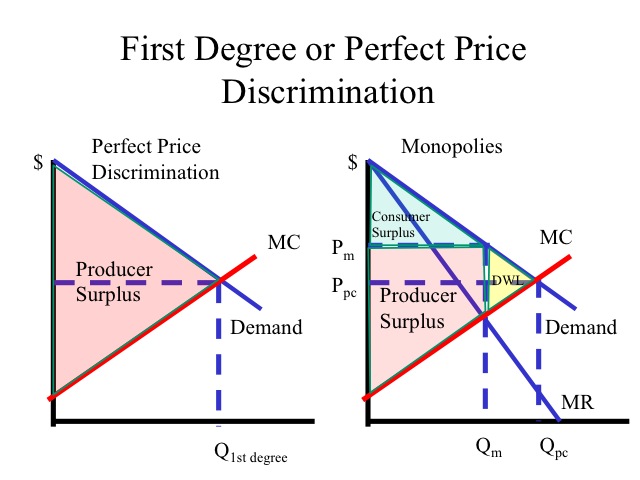
Understanding perfect price discrimination is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their pricing strategies in 2025. This concept, rooted deeply in economic theory, refers to the practice of charging each consumer the maximum price they are willing to pay. In this article, we will explore various aspects of perfect price discrimination, its methods, its implications on consumer surplus, and other related pricing techniques that can enhance businesses’ competitive advantage.
Understanding Types of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination can be categorized into three primary types: first-degree price discrimination, second-degree price discrimination, and third-degree price discrimination. Each type employs distinct strategies, suitable for different market conditions.
First-Degree Price Discrimination
First-degree price discrimination, also known as personalized pricing, allows businesses to charge each consumer the highest price they are willing to pay. This method requires in-depth understanding of individual preferences and behaviors. For instance, luxury automobile brands often utilize this technique by evaluating the financial capability and willingness to pay of each customer. This strategy can lead to enhanced profit maximization as firms tap into the varying demand curves of their consumers.
Second-Degree Price Discrimination
Second-degree price discrimination is based on the quantity purchased or the version of the product. For example, utility companies may offer discounts based on consumption levels – encouraging higher utility use through tiered pricing. This method not only enhances sales but also contributes to effective revenue management by catering to different consumer profiles.
Third-Degree Price Discrimination
In third-degree price discrimination, businesses segment consumers into distinct groups based on observable traits such as age or location. A common example is student discounts offered by many companies. This segmentation allows businesses to maximize profits while remaining competitive in monopolistic competition contexts.
The Role of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is a critical component in implementing effective pricing strategies. By understanding heterogeneous demand, businesses can tailor their pricing policies to meet specific needs, ensuring they capture all potential consumer surplus.
Geographical Pricing Strategies
Geographical pricing is a form of segmentation where prices vary based on the consumer’s location. This method can be advantageous in international markets where purchasing power varies significantly. Companies can adjust their prices according to local market dynamics while still maximizing revenues through targeted strategies.
Dynamic Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices based on real-time market demand. For instance, airline tickets often fluctuate based on the price elasticity of demand, helping airlines achieve optimum occupancy rates while maximizing revenue. This strategy relies heavily on data analytics, allowing businesses to respond proactively to market conditions.
Value-Based Pricing Techniques
Value-based pricing determines price based on consumer perceived value. This approach considers what customers believe a product is worth rather than its production cost, making it an efficient method in today’s market landscape. For example, software companies often follow this strategy, aligning their pricing with the value delivered to the consumer.
Challenges of Implementing Price Discrimination
While there are numerous benefits to price discrimination, including improved profitability and market insight, there are significant challenges that businesses face.
Ethical Concerns of Price Discrimination
Price discrimination raises various ethical concerns, particularly around fairness and equity. Critics argue that this practice exploits consumers, necessarily leading to a divide between different socioeconomic groups. Businesses must tread carefully, ensuring their pricing strategies do not biases against any particular group.
Legal Aspects of Price Discrimination
There are legal parameters governing pricing practices in many countries. Businesses need to be aware of laws surrounding price discrimination to avoid potential litigation. Regulatory bodies scrutinize pricing practices to ensure they align with fair trade and competition laws, providing a balance between profit maximization and consumer protection.
Impact on Market Dynamic
The impact of price discrimination on consumer behavior and overall market dynamics is significant. Consumers may react negatively to perceived unfair pricing, affecting brand loyalty and trust. Businesses need to utilize effective customer relationship management strategies to mitigate these impacts and ensure long-lasting customer loyalty.
Practical Examples of Price Discrimination in Action
Examining real-world cases of price discrimination can provide valuable insights into effective pricing strategies.
Case Study: Airline Industry
Airlines deploy various forms of price discrimination to manage their capacities effectively. With dynamic pricing, seats are often sold at varying prices depending on when they are booked, demand, and even the season. Furthermore, they utilize frequent flyer programs that incentivize customer loyalty while effectively segmenting price offered based on traveler behavior.
Case Study: Digital Products
In the realm of digital products, platforms like Amazon adjust prices dynamically based on user interaction, demand patterns, and competitors’ strategies. Through data analytics, they effectively employ customer segmentation strategies, offering personalized recommendations and pricing that align with individual consumer’s willingness to pay.
Case Study: Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS companies like Adobe implement tiered pricing structures, providing different software versions at various price points depending on the features offered. This not only addresses heterogeneous demand but also allows clients to select packages that best match their needs and budget.
Conclusion
Perfect price discrimination and its methods are unbiased opportunities for enhancing business profitability while ensuring consumer satisfaction in a competitive landscape. By mastering these strategies and understanding their implications on consumer behavior, companies can establish a formidable presence in dynamic markets. Incorporating advanced data analytics and segmentation strategies can further refine pricing approaches, cementing their competitive edge as we progress through 2025 and beyond.
Key Takeaways
- Perfect price discrimination allows businesses to maximize profits through personalized pricing strategies.
- Understanding various types of price discrimination, such as first, second, and third-degree, is essential for market segmentation.
- There are ethical and legal considerations surrounding price discrimination that businesses must navigate carefully.
- Pathways for applying price discrimination can be found in diverse industries including airlines, digital products, and SaaS.
- Data analytics and customer insights are crucial for implementing successful price discrimination strategies.
FAQ
1. What are the key benefits of perfect price discrimination?
The primary benefits of perfect price discrimination include enhanced profits, improved sales efficiency, and effective resource allocation. By charging each consumer according to their willingness to pay, companies can capture the entire consumer surplus, boosting overall revenue while potentially improving customer satisfaction through tailored pricing. Additionally, this method promotes efficient resource allocation in markets with heterogeneous demand.
2. How do ethical concerns affect price discrimination practices?
Ethical concerns surrounding price discrimination primarily revolve around fairness. Critics argue that it can lead to inequities, where consumers who can afford to pay more receive better prices or products, which may further socio-economic divides. Businesses must weigh these ethical implications carefully to align their pricing strategies with consumer perceptions of fairness and equity, ensuring long-term customer relationships.
3. What are the legal implications of different price discrimination methods?
Different types of price discrimination face varying legal restrictions across jurisdictions. For example, third-degree price discrimination might lead to challenges under anti-discrimination laws if perceived as unfairly targeting specific groups. Companies must ensure their pricing policies comply with relevant trade practices and remain transparent to avoid legal repercussions, engaging in market research to stay informed about regulatory changes.
4. Can price discrimination strategies adjust based on market dynamics?
Yes, price discrimination strategies can and should adjust continuously based on market dynamics and consumer behavior. Utilizing data analytics allows businesses to track changes in demand and customer preferences, enabling dynamic pricing strategies to adapt quickly, keeping the pricing model relevant and maximizing profit potential throughout different market conditions.
5. What role does customer loyalty play in price discrimination?
Customer loyalty plays a crucial role in successful price discrimination strategies. Loyal customers may be willing to accept higher prices for consistent value and service quality. Businesses can leverage this loyalty through targeted segmentation, offering discounts or special pricing in return for long-term commitment, thus solidifying consumer relationships and enhancing profitability in competitive markets.
“`