Effective Ways to Calculate the Area of a Pyramid in 2025: Get Started Now!
Effective Ways to Calculate the Area of a Pyramid in 2025: Get Started Now!
Pyramids are fascinating geometric shapes that are both simple and complex. Understanding how to calculate the area of a pyramid involves grasping several key concepts and formulas. This article will break down the essential methods and types of pyramids you need to know to accurately determine their area, volume, and surface area. The **pyramid area formula** plays a central role, and we’ll explore various aspects of pyramid geometry to clarify this important topic.
The Pyramid Area Formula
The **pyramid area formula** is a fundamental aspect of understanding pyramids in geometry. The area of a pyramid can be represented through its base area and lateral surface area. The formula usually combines the base area measurements and the slant height of the pyramid. The basic equation for calculating the total surface area, which includes the base and lateral areas, involves a clear understanding of these components.
Understanding Base Area and Pyramid Types
The **base area of a pyramid** varies depending on the shape of the base—it can be triangular, square, or polygonal. For a square pyramid, the base area can be calculated using the formula:
Base Area = side_length × side_length
For a triangular pyramid, known as a tetrahedron, the base area can be found using triangle area formulas. Understanding the **types of pyramids** and their respective base areas is crucial, as it significantly impacts the overall area calculation of the pyramid.
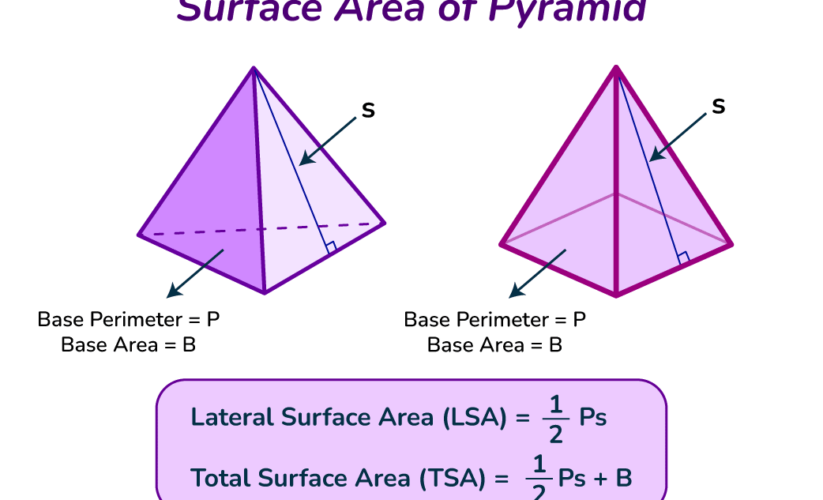
Lateral Surface Area of a Pyramid
The **lateral surface area of a pyramid** consists of the areas of its triangular faces, which connect the base to the apex of the pyramid. The formula to calculate the lateral surface area depends on the perimeter of the base and the slant height of the pyramid:
Lateral Surface Area = (Base Perimeter × Slant Height) / 2
Knowing how to determine the **slant height of a pyramid** is essential, as it sometimes requires calculating using geometric principles involving the height of the pyramid and half the base’s width.
Pyramid Volume Insights
Pyramid volume calculations are incredibly important in both mathematics and real-world applications, particularly in architecture and construction. The **pyramid volume formula** is as follows:
Volume = (1/3) × Base Area × Height
This formula emphasizes the significance of both the **height of a pyramid** and its base area, linking the concepts of area and volume closely together.
Applications of Pyramid Volume in Real Life
<pUnderstanding the **volume of a triangular pyramid** is crucial in various architectural designs and construction projects. For example, when creating modern structures that replicate pyramids, builders often rely on accurate pyramid volume calculations to ensure stability and spatial integrity. This application demonstrates just how valuable **pyramids in architecture** can be.
Moreover, practical case studies show that effective **calculating pyramid volume** supports planners during the construction of monumental buildings or even for smaller-scale projects such as landscaping designs that utilize symmetrical elements.
Determining Height and Volume
Calculating the **height of a pyramid** can present challenges, especially if only base measurements are accessible. To find the height, you may employ the Pythagorean theorem, especially in right-angled triangles involving the slant height:
Height = √(Slant Height² – (Base Width/2)²)
This is an effective method to understand the geometry of pyramids and applies both to triangular and square bases. Mastering these calculations is fundamental for accurately applying the **pyramid volume formula** and ensuring correctness in further studies of **pyramid area calculations**.
Exploring Types of Pyramids
The world of pyramids includes several varieties such as **polygonal pyramids** and **triangular pyramids**. Each has distinct characteristics and is scrutinized differently in geometry, affecting their area and volume calculations. Understanding these different types enhances the comprehension of **pyramid geometry**.
Geometric Principles of Different Pyramid Shapes
Different shapes in pyramids, such as a **square pyramid** and a triangular pyramid, place varying demands on calculations involving areas and volumes. For instance, a **square pyramid**’s geometry has symmetrical properties that ease calculations, while **triangular pyramid** calculations may involve more intricate triangulation based on base dimensions.
Understanding Composite Shapes with Pyramids
**Composite shapes with pyramids** often appear in larger geometric configurations where various geometric figures come together. For architects and engineers, utilizing these principles allows them to design innovative structures, enhancing their designs with layered uses of **pyramids in construction**. Calculating the cross-section areas and integrating them effectively is essential for efficiency in both theoretical studies and practical applications.
Conclusion
In summary, the calculation of the area of pyramids encompasses multiple facets, including various formulas, the impact of different shapes, and their real-world applications. Understanding the relationship between the **height and volume of a pyramid**, alongside mastering the technical aspects of the **pyramid area formula**, can greatly enhance mathematical skills and application potential in various fields, such as architecture and engineering. Now, diving deeper into these concepts will create a clearer path for effective geometry use and practical implementation.
Key Takeaways
- The **pyramid area formula** is key for determining total surface area, which incorporates both base area and lateral surface area.
- Understanding the unique properties of different pyramid shapes eases volume and area calculations significantly.
- Practical applications in architecture place emphasis on accurate area and volume calculations to ensure foundational stability.
FAQ
1. What are the different types of pyramid bases?
The **types of pyramid bases** include triangular, square, pentagonal, and other polygonal shapes. Each base type influences the calculations for both area and volume, requiring specific formulas based on the geometric parameters of the base used.
2. How do you calculate the lateral area of a pyramid?
To calculate the **lateral surface area of a pyramid**, you will need to know the perimeter of the base and the slant height. The formula is (Base Perimeter × Slant Height) / 2, which provides a clear metric for determining the area of the triangular faces of the pyramid.
3. Can you derive the pyramid volume formula?
Yes, the **pyramid volume formula** can be derived from the base area and height. Taking the cross-sectional area into account, we find that the volume is proportional to the height and base area: Volume = (1/3) × Base Area × Height. This relationship is a crucial aspect of solid geometry.
4. What impact do the properties of pyramids have in architecture?
The **properties of pyramids** are essential in architecture, providing designers with foundational stability and aesthetic appeal. They often serve as visual focal points in historic and modern structures, showcasing the integration of geometrical principles in design work.
5. How can I improve my understanding of pyramid geometry?
Improving your understanding of **pyramid geometry** can involve studying various types, their properties, and practical applications. Engaging with mathematical resources that focus on solid shapes and utilizing educational software can significantly enhance your grasp of geometric concepts.
6. What mathematical proofs relate to pyramids?
Numerous **mathematical proofs** concern pyramids which can explore their volume, surface area, and properties through various methodologies. Each proof reinforces theoretical grounding in geometric principles and educates on practical applications.
7. How do you measure the slant height of a pyramid?
To measure the **slant height of a pyramid**, you can use the Pythagorean theorem. In a right triangle formed from the height, half the base width, and the slant height, if you know the height of the pyramid and half the base width, the slant height can be easily calculated to ensure better accuracy in area calculations.